System Processing Tools Below: Decision Trees and Decision Tables
- Decision Trees and Decision Tables are two very important System Processing Tools.
Decision Tree
Introduction
- Decision trees are a powerful tool for both classification and regression tasks, providing a clear and interpretable model.
- By understanding the structure and functioning of decision trees, one can effectively apply them to various decision-making and predictive modeling tasks.
Definition
- A decision tree is a graphical representation used to make decisions and predict outcomes by mapping various possible choices and their possible consequences.
Components of a Decision Tree
The following major components are used in making a decision tree:-
- Root Node:
-
The topmost node in a decision tree represents the entire dataset or the initial question that needs to be answered.
-
-
Decision Nodes:
-
These internal nodes represent decision points or tests on an attribute.
-
-
Branches:
-
This is the connectors between nodes that represent the outcome of a decision or test.
-
Example: “Yes” or “No” based outcomes.
-
-
Leaf Nodes (Terminal Nodes):
-
Endpoints of a decision tree that represent the outcome or decision.
-
Working Mechanism
- Decision trees operate by recursively splitting the data into subsets based on the value of input attributes.
- This process continues until all data is classified or a stopping criterion is met.
- The tree structure allows easy interpretation of the decision-making process.
Types of Decision Trees
-
Classification Trees:
-
This decision tree is used when the output is a categorical variable.
-
The tree classifies the input data into predefined classes.
-
Example: Determining whether an email is “Spam” or “Not Spam”.
-
-
Regression Trees:
-
This decision tree is used when the output is a continuous variable.
-
The tree predicts the value of the output variable based on the input variables.
-
Example: Predicting the price of a house based on its features.
-
Advantages of Decision Trees
- Decision trees are intuitive, simple to understand & interpret, and easy to visualize, making them accessible to non-experts.
- Decision trees do not require the normalization of data, making them straightforward to apply.
- Decision trees can handle different types of input data, making them versatile.
Disadvantages of Decision Trees
- Decision trees can easily overfit the training data, capturing noise instead of the underlying pattern.
- Small changes in the data can result in significantly different trees, making them less stable.
- If some classes dominate, the tree might become biased towards the dominant class.
Tools and Libraries for Decision Trees
- Scikit-learn: It is a popular machine-learning library in Python that provides implementations of decision trees.
- R: It offers packages like
rpartandpartyfor building decision trees. - Weka: It is a data mining software that includes decision tree algorithms.
Example of a Decision Tree
(i) A decision tree for deciding whether to play outside based on weather conditions:
Root Node: Is it sunny?
-
- Decision Node: Yes
- Decision Node: Is it hot?
- Leaf Node: Yes -> Stay inside
- Leaf Node: No -> Play outside
- Decision Node: Is it hot?
- Decision Node: No
- Leaf Node: Stay inside
- Decision Node: Yes
(ii) A graphical representation/example of the decision tree are –
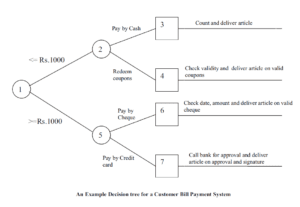
Use/Applications
- It is widely used in data mining, machine learning, and decision analysis.
Decision Table
Introduction
- Decision tables are an effective tool for modeling complex decision-making scenarios in a structured and comprehensive way.
Definition
- A Decision Table is a tabular method for representing and analyzing decision rules and provides a systematic way to identify and document various conditions and the corresponding actions to take based on those conditions.
-
A decision table shows the way the system handles input conditions and subsequent actions on the event.
Characteristics
- They enhance clarity, ensure consistency, and facilitate effective documentation and testing of decision rules.
- Decision tables are particularly useful in complex decision-making processes where multiple conditions and actions need to be considered simultaneously.
Components of a Decision Table
- A decision table is composed of rows and columns, separated into four separate quadrants.
| Input Conditions | Condition Alternatives |
| Actions | Subsequent action Entries |
- There are the following components used or focussed during the creation of a Decision Table –
-
- Conditions:
- These are the different scenarios or criteria that need to be evaluated.
- Actions:
- These are the possible outcomes or decisions that will be executed based on the conditions.
- Condition Entries:
- These are the possible states or values for each condition.
- Action Entries:
- These are the specific actions to be taken for each set of conditions.
- Conditions:
Structure of a Decision Table
A typical decision table consists of four quadrants:-
- Conditions Stub: It lists/includes all the conditions.
- Actions Stub: It lists/includes all the possible actions.
- Conditions Entries: It specifies the values for each condition in different scenarios.
- Actions Entries: It indicates the actions to be taken for each combination of condition values.
Example of a Decision Table
A simplified example of a decision table for an online store’s order processing system is:-
| Conditions | Rule 1 | Rule 2 | Rule 3 | Rule 4 |
| Customer Type | New | New | Existing | Existing |
| Order Amount > 500 | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Actions | ||||
| Offer Discount | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Free Shipping | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Priority Handling | No | Yes | No | Yes |
In this table:
- Customer Type and Order Amount > 500 are the conditions.
- Offer Discounts, Free Shipping, and Priority Handling are the actions.
- The rules specify different combinations of conditions and the corresponding actions.
Benefits of Decision Tables
- They provide a clear and concise way to represent complex decision logic.
- It helps to ensure that all possible combinations of conditions are considered, reducing the likelihood of missing a condition.
- It is a formal documentation of business rules, which is useful for auditing and compliance.
- It facilitates the creation of test cases for software testing by clearly defining the input conditions and expected outputs.
Working Steps to Create a Decision Table
- Identify Conditions: First of all list all the conditions that affect the decision-making process.
- Identify Actions: Now, list all the possible actions that can be taken.
- Define Condition Entries: Now, determine the possible values or states for each condition.
- Define Action Entries: Now, specify the actions to be taken for each combination of condition values.
- Review and Simplify: Check for any redundant rules or conditions and simplify the table if possible.
Use/Applications of Decision Tables
- Business Rules Modeling: It helps in capturing complex business rules in the insurance, finance, and healthcare sectors.
- Software Engineering: It is used to specify logic for system behavior, especially in rule-based systems.
- Testing and QA: It creates comprehensive test cases to ensure all scenarios are covered.
System Processing Tools above: Decision Trees and Decision Tables.
![]()
0 Comments